Have you ever wondered how exercise affects your metabolism and helps with weight management? In this article, we will explore the fascinating connection between physical activity, metabolism, and maintaining a healthy weight. From the way exercise increases metabolism to the long-term benefits of regular workouts, we’ll uncover the impact that exercise can have on your overall well-being. So, lace up those sneakers and get ready to discover the positive effects of staying active on your metabolism and weight management journey.
The Role of Metabolism in Weight Management
When it comes to weight management, understanding the role of metabolism is crucial. Metabolism refers to the chemical processes that occur within the body to maintain life. It is responsible for converting the food we consume into energy, which is then used for various bodily functions. Essentially, metabolism determines how many calories our bodies burn at rest and during physical activity.
Definition and Function of Metabolism
Metabolism can be categorized into two main components: basal metabolic rate (BMR) and physical activity. BMR refers to the number of calories burned at rest, i.e., the energy required for essential bodily functions such as breathing, circulating blood, and maintaining body temperature. Physical activity, on the other hand, includes any bodily movement that requires energy expenditure, such as exercise or daily activities.
The function of metabolism is to regulate energy balance in the body. When we consume more calories than our bodies need for daily activities, the excess energy is stored as fat. Conversely, when we consume fewer calories than our bodies require, the stored fat is utilized as an energy source, leading to weight loss.
Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
Basal metabolic rate (BMR) accounts for the majority of calories burned each day. It is influenced by several factors, including age, gender, genetics, body composition, and hormone levels. Generally, men tend to have a higher BMR than women due to higher muscle mass and testosterone levels. As we age, our BMR tends to decrease, mainly due to muscle loss and hormonal changes.
To maintain weight, it is essential to balance calorie intake with BMR. If calorie intake exceeds BMR, weight gain is likely to occur. Conversely, if calorie intake is lower than BMR, weight loss is more probable. Understanding and effectively managing BMR is crucial for weight management.
Effect of Metabolism on Weight Gain and Loss
Metabolism plays a significant role in weight gain and loss. If you have a fast metabolism, you are more likely to burn calories efficiently, which can aid in weight maintenance or weight loss. However, if you have a slow metabolism, your body may store more calories as fat, making weight management more challenging.
While genetics and other individual factors can influence metabolism, exercise can play a vital role in modulating and optimizing metabolic rate. Regular physical activity has the potential to boost metabolism, increase energy expenditure, and promote weight loss.
Exercise and Its Effects on Metabolism
Exercise has numerous benefits for metabolism and weight management. It can significantly increase energy expenditure, leading to a higher calorie burn both during and after the workout. Additionally, exercise can stimulate metabolic adaptations that enhance overall metabolic efficiency, making weight loss more sustainable in the long term.
Increased Energy Expenditure
One of the primary effects of exercise on metabolism is increased energy expenditure. When you engage in physical activity, your body requires more energy to fuel the muscles and perform various movements. As a result, your metabolic rate temporarily rises, leading to a higher calorie burn. While the exact increase in energy expenditure may vary depending on the type and intensity of exercise, incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can have a significant impact on weight management.
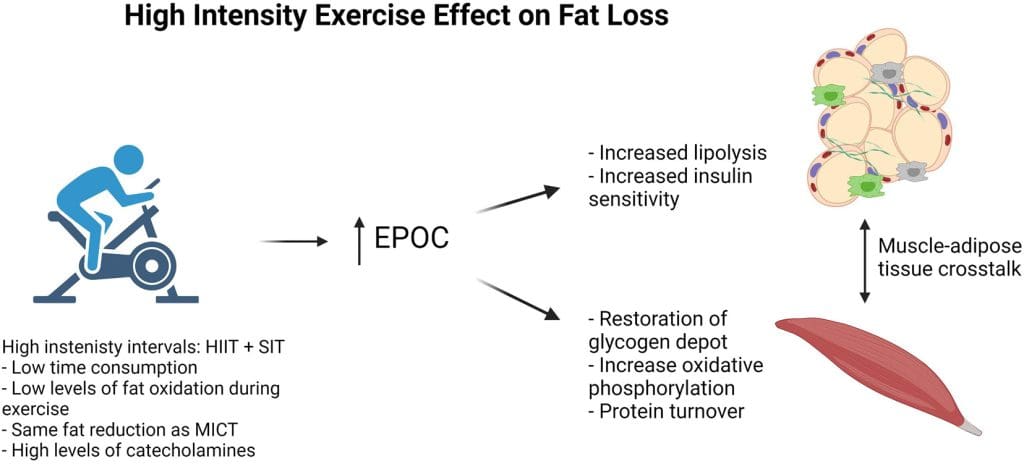
EPOC (Excess Post-Exercise Oxygen Consumption)
Another way exercise affects metabolism is through excess post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC). After a workout, your body continues to consume oxygen at an elevated rate to restore and repair muscle tissues, replenish energy stores, and remove metabolic waste products. This increased oxygen consumption contributes to additional calorie burn even after you’ve finished exercising. The intensity and duration of the workout can influence the magnitude and duration of EPOC, making high-intensity exercises particularly effective for boosting metabolism.
Metabolic Adaptations to Exercise
Regular exercise can also lead to metabolic adaptations that improve overall metabolic efficiency. Your body becomes more efficient at utilizing and metabolizing nutrients, including carbohydrates and fats, for energy production. This increased efficiency can contribute to weight loss and make it easier to maintain a healthy weight in the long run. Additionally, exercise can promote the development and preservation of lean muscle mass, which can further enhance metabolic rate and calorie burn.
Types of Exercise and Their Impact on Metabolism
Different types of exercise have varying effects on metabolism. Incorporating a combination of cardiovascular exercise, resistance training, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT) can optimize metabolic rate and weight management.
Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardiovascular exercise, such as running, cycling, or swimming, can have a significant impact on metabolism. It increases heart rate and breathing rate, leading to a higher calorie burn during the activity. Cardiovascular exercise also improves cardiovascular health, endurance, and overall fitness, enhancing your body’s ability to utilize oxygen and fuel sources efficiently.
Resistance Training
Resistance training, also known as strength training or weightlifting, is essential for building and preserving lean muscle mass. While resistance training may not burn as many calories during the workout as cardiovascular exercise, it has a lasting impact on metabolism. As you gain more muscle, your BMR increases, resulting in a higher calorie burn even at rest. Additionally, resistance training can help prevent muscle loss during weight loss, making it an integral part of any comprehensive exercise program.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) involves short bursts of intense exercise followed by brief recovery periods. This type of exercise can significantly elevate heart rate and metabolic rate, leading to increased calorie burn both during and after the workout. HIIT workouts are known to be time-efficient and can provide numerous health benefits, including improved cardiovascular fitness and enhanced metabolic efficiency.
Effect of Different Exercise Intensities on Metabolism
The intensity of exercise plays a role in determining its impact on metabolism. Higher-intensity exercises, such as HIIT, generally result in a greater calorie burn and metabolic boost compared to low-intensity exercises. However, it’s important to note that any form of physical activity can contribute to weight management and improved metabolic health. The key is finding a balance between different exercise intensities and incorporating a variety of activities into your routine.
Long-Term Effects of Exercise on Metabolism
Exercise can have profound long-term effects on metabolism, making it an invaluable tool for weight management and overall health.
Maintenance or Increase of Lean Muscle Mass
Regular exercise, particularly resistance training, can help maintain or increase lean muscle mass. As mentioned earlier, having more muscle mass leads to a higher BMR, resulting in increased calorie burn at rest. By preserving or building muscle, you can enhance your metabolic rate and make weight management more sustainable in the long run.
Boosting Resting Metabolic Rate (RMR)
Resting metabolic rate (RMR) is similar to BMR but includes the energy expended during periods of rest rather than only at complete rest. Regular exercise can boost RMR, enabling your body to burn more calories throughout the day, even when you’re not actively engaged in physical activity. This increase in RMR can have a significant impact on weight management, making it easier to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Prevention of Metabolic Slowdown
Metabolic slowdown refers to the decrease in metabolic rate that often occurs during weight loss efforts. When you reduce your calorie intake for an extended period, your body may respond by conserving energy and decreasing metabolic rate. However, regular exercise can help prevent or minimize this metabolic slowdown by signaling to your body that the increased energy expenditure is necessary. By maintaining an active lifestyle and incorporating exercise into your routine, you can avoid a significant drop in metabolic rate and make weight management more successful.
Exercise and Basal Metabolic Rate (BMR)
While exercise primarily affects RMR, it can indirectly influence BMR as well. By increasing muscle mass and improving overall metabolic efficiency through exercise, your BMR can be positively impacted. This means that even at complete rest, your body will burn more calories, helping to maintain weight or achieve weight loss.
Exercise as a Tool for Weight Loss
Exercise is a powerful tool for weight loss, as it promotes calorie expenditure and fat burning.
Caloric Expenditure and Weight Loss
Weight loss occurs when calorie expenditure exceeds calorie intake. Through physical activity, exercise increases calorie expenditure, creating an energy deficit that leads to weight loss. While exercise alone may not be sufficient for significant weight loss, it can play a crucial role when combined with a balanced diet and other healthy lifestyle habits.
Exercise and Fat Burning
Exercise promotes fat burning by utilizing stored fat as an energy source. During prolonged exercise sessions, your body relies on fat stores for energy, gradually reducing body fat percentage. Additionally, high-intensity exercises, such as HIIT, can result in increased fat oxidation and improved metabolic flexibility, making it easier for your body to switch between different fuel sources.
Combining Exercise with a Balanced Diet
To optimize weight loss and overall health, it’s important to combine exercise with a balanced diet. Physical activity alone may not be sufficient to achieve significant weight loss if calorie intake remains high. By adopting a nutritious and calorie-controlled diet, you can ensure that your body receives the necessary nutrients while creating a calorie deficit for weight loss. Exercise complements this approach by increasing energy expenditure and promoting fat burning.
Exercise for Long-Term Weight Management
While exercise can contribute to initial weight loss, its true value lies in long-term weight management. By incorporating regular exercise into your lifestyle, you can maintain a healthy weight, prevent weight regain, and improve metabolic health. Engaging in enjoyable and sustainable physical activities can make weight management more enjoyable and create a positive relationship with exercise.
Factors That Influence the Impact of Exercise on Metabolism and Weight Management
Several factors can influence how exercise affects metabolism and weight management. Understanding these factors can help you tailor your exercise routine to maximize results.
Age and Metabolism
Age can significantly influence metabolism and the body’s response to exercise. As we age, our metabolism tends to slow down, primarily due to a decrease in muscle mass and changes in hormone levels. However, regular exercise can help counteract these age-related metabolic changes and maintain a healthy metabolism. It is important to adjust exercise routines to accommodate any age-related limitations and focus on activities that promote muscle growth and metabolic efficiency.
Genetics and Metabolic Rate
Genetics can influence individual metabolic rates, meaning some people naturally have faster or slower metabolisms. While genetics can play a role in weight management, it is not destiny. Regardless of your genetic predispositions, regular exercise can positively impact metabolism and weight management. By focusing on physical activity that increases calorie burn and promotes muscle growth, you can optimize your metabolic rate and achieve a healthy weight.
Gender Differences in Metabolic Response to Exercise
Men and women may have different metabolic responses to exercise due to inherent physiological differences. Generally, men tend to have a higher BMR and greater muscle mass, leading to a higher calorie burn at rest. However, women may have a higher capacity for fat oxidation during exercise, which can contribute to enhanced weight loss. Understanding these gender differences can help tailor exercise routines to maximize metabolic benefits.
Effect of Exercise Duration and Frequency
The duration and frequency of exercise also play a role in its impact on metabolism and weight management. While any amount of physical activity is beneficial, longer and more frequent exercise sessions generally result in greater calorie burn and metabolic improvements. However, it’s important to find a balance that works for your lifestyle and allows for consistency. Consistency is key when it comes to exercise, and incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is more important than focusing solely on duration or frequency.
The Importance of Consistency and Variety in Exercise Regimen
Consistency and variety are crucial when it comes to creating an effective and sustainable exercise regimen.
Creating Sustainable Exercise Habits
Consistency is paramount in creating sustainable exercise habits. It’s essential to find activities that you enjoy and can realistically incorporate into your daily routine. By making exercise a regular part of your life, it becomes a habit rather than a chore. Set achievable goals, start small, and gradually increase the duration and intensity of your workouts to avoid burnout and maintain long-term consistency.
The Role of Cross-Training
Cross-training involves incorporating a variety of exercises and activities into your routine. By engaging in different types of exercise, you can target various muscle groups, prevent overuse injuries, and maintain motivation and interest. Cross-training also promotes overall fitness and improves cardiovascular health, enhancing the effectiveness of your workouts.
Periodization and Metabolic Adaptation
Periodization is a training technique that involves varying the intensity, duration, and type of exercise over specific periods. This approach helps prevent plateaus in progress and encourages continued metabolic adaptations. By constantly challenging your body with different exercise stimuli, you can optimize metabolism and maximize weight management results. Periodization can be applied to both cardiovascular and resistance training exercises, allowing for continual improvement and sustained progress.

Exercise and Metabolic Disorders
Exercise can have significant benefits for individuals with metabolic disorders, such as insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and certain thyroid disorders.
Exercise for Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Regular exercise is essential for individuals with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Physical activity improves insulin sensitivity, allowing for better glucose uptake and utilization. Exercise also promotes weight loss, reduces the risk of cardiovascular complications, and improves overall metabolic health. It is crucial for individuals with these conditions to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an exercise plan that is safe and effective.
Exercise and Metabolic Syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a cluster of conditions that can increase the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. These conditions include high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess body fat (especially around the waist), and abnormal cholesterol levels. Regular exercise can significantly improve the symptoms of metabolic syndrome by reducing blood pressure, improving insulin sensitivity, promoting weight loss, and lowering cholesterol levels.
Exercise for Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or an underactive thyroid, can impact metabolism and weight management. While exercise alone cannot cure thyroid disorders, it can support overall metabolic health and aid in weight management. Physical activity can increase energy expenditure, improve mood and energy levels, and prevent weight gain associated with an underactive thyroid. Individuals with thyroid disorders should work closely with their healthcare providers to develop an exercise plan that is suitable for their specific needs.
The Psychological and Emotional Benefits of Exercise for Weight Management
Exercise offers numerous psychological and emotional benefits that support weight management.
Reduction of Stress and Emotional Eating
Regular exercise has been shown to reduce stress levels by increasing endorphin production in the brain. Engaging in physical activity can serve as a healthy outlet for stress and emotions, preventing the use of food as a coping mechanism. By incorporating exercise into your routine, you can better manage stress and reduce the likelihood of emotional eating, which can contribute to weight gain.
Improvement in Mood and Self-esteem
Exercise has a profound impact on mood and self-esteem. Physical activity stimulates the release of endorphins, known as “feel-good” hormones, which can enhance mood and overall well-being. Regular exercise also promotes self-confidence and self-esteem by improving body image, increasing physical fitness, and achieving personal goals. By feeling good about yourself, you are more likely to engage in positive behaviors, such as maintaining a healthy weight.
Exercise and Sleep
Regular exercise can improve sleep quality and duration, which is essential for overall health and weight management. Physical activity increases the production of serotonin, a hormone that regulates sleep-wake cycles. By engaging in exercise earlier in the day, you can promote better sleep hygiene and create a positive cycle of increased energy, productivity, and improved weight management.
Conclusion
Exercise plays a critical role in metabolism and weight management. By understanding the impact of exercise on metabolism, individuals can utilize physical activity as a tool for weight loss and long-term weight management. Through increased energy expenditure, metabolic adaptations, and promotion of overall health, exercise can optimize metabolic rate and enhance weight management efforts. It is important to prioritize consistency, variety, and individualization when developing an exercise routine, considering factors such as age, genetics, and existing metabolic disorders. By incorporating regular exercise into your lifestyle, you can achieve a healthy weight, improve metabolic health, and experience the countless physical and psychological benefits that come with an active lifestyle.
